AKI following PNC exposure
medcases00
Published on Oct 28, 2021
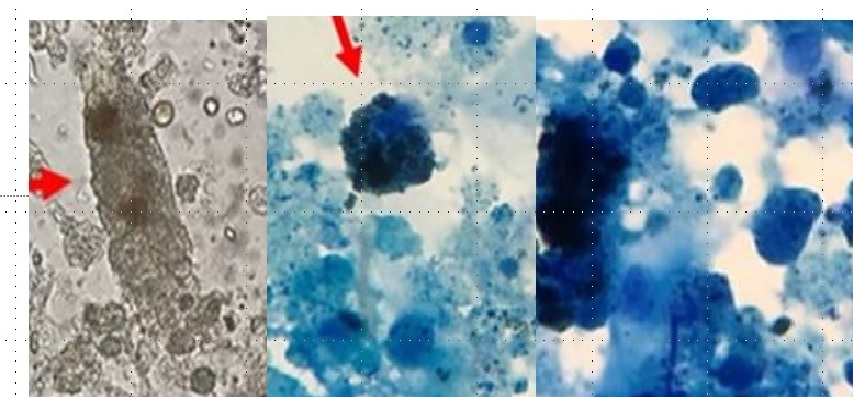
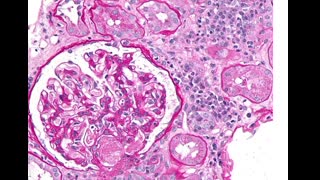
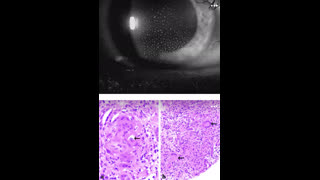
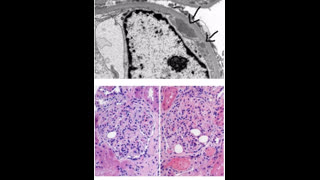
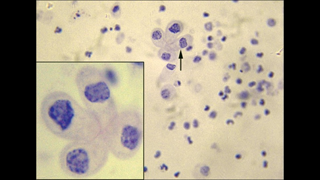
A 25-year-old woman presented to a hospital with fatigue, SOB , dark urine for past 1 week. . Dipstick urinalysis protein 3+, hemoglobin 3+, urobilinogen positive, and bilirubin 1+. Urine microscopy shows epithelial cells (RTECs) (>40/high power field), 6-7 RBC cells , granular casts (4-5/lower power field) and RTEC casts (1–2/lower power field)., urine eosinophils positive, BUN 65, creatinine of 3.31 mg/dl, hemoglobin 6.4g/dl, hematocrit 25%, and platelets 182,000/μl. CPK level normal , LDH was high, TBR is 2.0, Direct BR is 1.3, AST, ALT normal but serum haptoglobin was low - She was recently started on amoxicillin for UTI 2 weeks before admission. May–Grünwald–Giemsa stain of urine specimen is above. She refused renal biopsy and was started on prednisone empirically. Her creat improved to 1.2 range after 2 weeks of steroid treartment.
what is likely cause of acute kidney injury -?
a) Acute allergic interstitial nephritis
b) heme induced acute kidney injury
c) Bilirubin cast nephropathy
d) rhabdomyolysis.
e) ATN from drug induced.
Explanation
Answer is ( b) . AKI is due to haem induced acute kidney injury caused by cephalexin which has been associated with hemolytic anemia, AIN and ATN. Intravascular hemolysis results in release of hemoglobin/heme into the circulation, and is filtered in the nephrons,. haem moiety is nephrotoxic and causes cell injury and death in the renal tubular cells. Dark urine can be a sign of urinary pigment due to rhabdomyolysis, hyperbilirubinuria, or hemolytic anemia. low haptoglobin, high direct BR levels, high LDH level are suggestive of autoimmune hemolytic anemia due to drug exposure ( cephalexin). urine sediment shows RTECs, pigmented granular casts, and RTEC casts suggesting ATN mediated by iron deposits within RTECs. Urine sediment image shows Urinary cast with iron deposits which is well stained on May–Grünwald–Giemsa stain. Numerous iron deposits (hemosiderin granules) seen within the casts
AIN is less likely . urine eosinophils being high is not diagnostic - fever, rash, eosinophilia is the classic triad, UA showing wbc casts would be more supportive of AIN, bile cast nephropathy is significantly correlated with higher serum total and direct bilirubin levels, and a trend toward higher serum creatinine, AST, and ALT levels. Bile casts may contribute to the kidney injury of severely jaundiced patients by direct bile and bilirubin toxicity, and tubular obstruction. CPK Level being normal rules out rhabdomyolysis.
Reference
Longstreth KL, Robbins SD, Smavatkul C, Doe NS: Cephalexin-induced acute tubular necrosis. Pharmacotherapy 24: 808–811, 2004PubMedGoogle Scholar
Thiessen K, Kraleti S: Cephalexin-induced haemolytic anaemia: A case report. J Clin Pharm Ther 42: 615–617, 2017Google Scholar