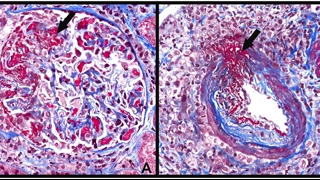
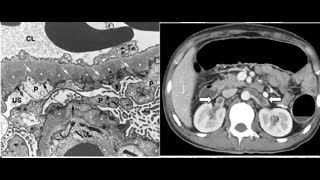
35 year old lady post renal transplant with diarrhea, weight loss and anasarca.
medcases00
Published on Aug 25, 2021
. A35 -yr-old African American woman with type 1 DM and a panel reactive antibody of 65% receives
her third renal transplant. Her immunosuppressive medications are tacrolimus, MMF, and prednisone.
Her creatinine is 1.7 range after 9 weeks . After 11 months of transplant she presents with of fatigue
and severe diarrhea for the past month. Her diarrhea was watery, non-bloody, occurring six times a day and unrelieved by intermittent loperamide use. She denied any sick contacts or recent travel. Her medical history consisted of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection, genital herpes and Kaposi sarcoma
(excised).She has whole body anasarca, abdominal ascites and 3+ pitting edema in her lower extremities bilaterally up to the knees and lower back. Her labs were significant for hypoalbuminemia(2.1g/dL; normal 3.5-4.8g/dL), and hypereosinophilia (absolute eosinophil 1.4K/uL; normal 0-0.5K/uL).
Urinalysis was negative for hematuria and proteinuria. Tacrolimus level was 9.9ng/mL (normal 5-20ng/mL).An infectious gastroenteritis workup including ova and parasites, stool culture including Salmonella, Shigella,Campylobacter and Clostridium difficile was negative. Serum tissue
transglutaminase and stool lactoferrin,
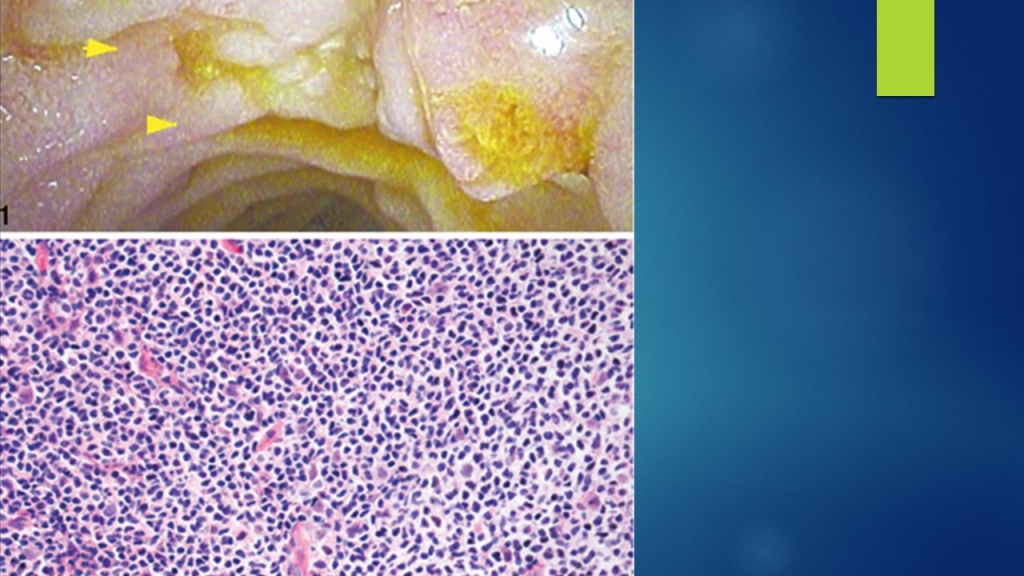
pancreatic elastase and calprotectin were unremarkable. Liver enzymes were within normal limits. EGD showed duodenal with lymphoproliferative disease on histology
NEXT STEP IN MANAGEMENT IS
A. Reduced Immunosuppression
B. Stop Immunosuppression .
C. Rituximab should be started and
immunosuppression maintained at its current levels.
D. reduce Immunosuppression and start valcyte
E. Surgical resection of the lesion
Answer is A
A) Epstein-Barr virus–has been associated with posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disease due to chronic IS . Therapeutic interventions that have been used in the treatment of PTLD include the reduction of immunosuppression, antiviral therapy ,Rituxan, chemotherapy, radiation, and surgical resection. The reduction of immunosuppression forms the cornerstone of all treatment and may be sufficient by itself, with complete remission in 63% of cases in some reports. The Best approach would be to reduce her overall immunosuppression and monitor her response.
B) Withdrawal of immunosuppression will almost certainly result in acute rejection due to her high PRA pre transplant
C). Rituximab has been shown to induce remission in transplant recipients, and can be considered in association with reduction of immunosuppression
D) While valcyte may be used for primary prophylaxis and reduced the incidence of PTLD by reducing viral loads, it’s use has not been effective
in the treatment of PTLD.
E) Surgical resection is not right option as disease can treated with reduction of IS regimen +/- chemotreatment
Reference
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25655616/