HIV patient with PNA and Worsening creatinine
medcases00
Published on Jul 21, 2021
CC- cough, fever in HIV patient.
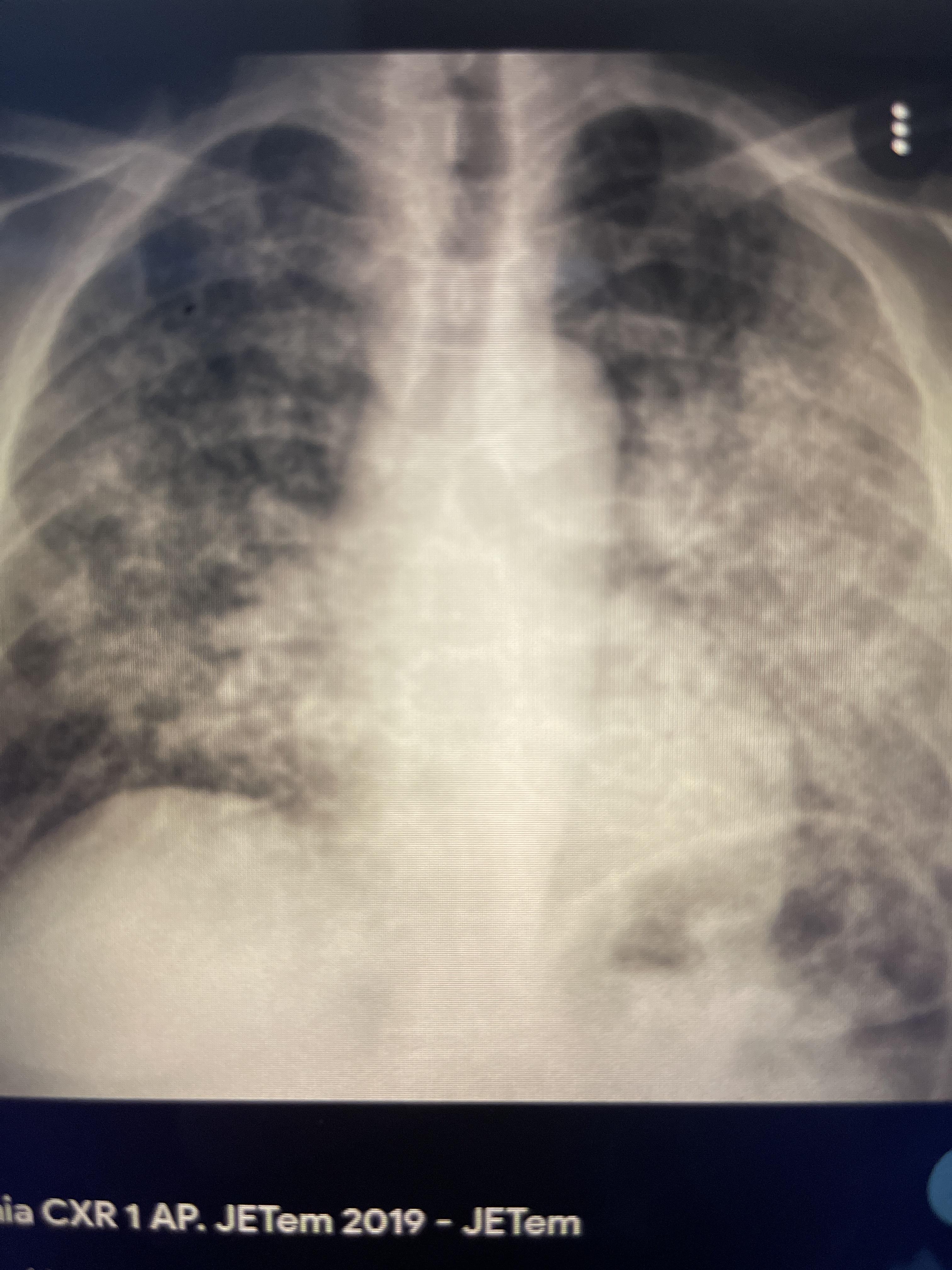
HPI - A 37 year old man with the acquired immunodeficiency
syndrome (AIDS) is hospitalized with a cough, fever, and a
perihilar pulmonary infiltrate on CXR. Therapy is initiated with
trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole due to PCP pna suspicion
LABS - On admission, the serum creatinine is 1.3 mg/dL and BUN 24 mg/dL;
follow up routine labs 5 days later, Cr is 2.4 mg/dL and blood urea nitrogen,
26 mg/dL, Results of urinalysis both on admission and 3 days later are normal.
Urine output on day 5 is 1250 mL.
The most likely cause of the increased creatinine is:
– A.) AIDS glomerulopathy - HIV nephropathy/HIVIC
– B.) Trimethoprim-mediated decrease in creatinine secretion
– C.) Intratubular obstruction secondary to sulfonamide
– D.) AIN caused by trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole therapy
– E.) Acute tubular necrosis secondary to sepsis
Scroll below for Answer
Correct answer is B
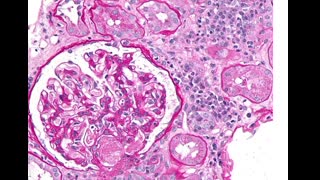
Elevated creatinine, no change in BUN, no evidence of ARF suggests inhibition of tubular secretion by Bactrim. Allergic interstitial nephritis typically presents with AKI, fever, rash, WBC in urine and peripheral eosinophilia induced by sulfa moiety . HIV-associated nephropathy (HIVAN), HIV immune complex kidney disease (HIVICK), and HIV-associated thrombotic microangiopathy can all present with AKI . HIVAN is a collapsing form of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) with associated tubular microcysts and interstitial inflammation. HIVAN classically presents with significant proteinuria and rapidly progressive kidney disease in the setting of normal blood pressure and normal to enlarged kidneys. A number of immune complex kidney diseases have been reported in patients with HIV infection, including membranous nephropathy, membranoproliferative and mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis, "lupus-like" proliferative glomerulonephritis, and immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy . Rarely, crystallization of sulfamethoxazole metabolite can cause intratubular obstruction. however relatively short duration of use makes it less likely cause.
REFERENCES
HIV-Associated Nephropathy: Clinical Presentation, Pathology, and Epidemiology in the Era of Antiretroviral Therapy- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2656916/
StatPearls - HIV Nephropathy-https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559134/
HIV associated nephropathy: a treatable condition- https://sti.bmj.com/content/77/2/97